SOME PAINFUL CONSEQUENCES OF HUMANITY’S DELUSIONS
SOIL POLLUTION IS RESPONSIBLE FOR 20% OF AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTIVITY LOSS
Soil pollutions – definition and some facts
“Soil pollution is a chemical degradation process that consumes fertile soils, with implications for global food security and human health. Soil pollution hampers the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including achieving zero hunger, ending poverty, ensuring healthy lives and human well-being, halting and reversing land degradation and biodiversity loss, and making cities safe and resilient. Most contaminants originate from human activities and enter into the environment because of unsustainable production chains, consumption patterns or inappropriate waste disposal practices.
In May 2018, FAO and its Global Soil Partnership (GSP), the World Health Organization (WHO), the Secretariat of the Basel, Rotterdam and Stockholm Convention and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) organized the Global Symposium on Soil Pollution (GSOP18) to bring together science and policy to understand the status, causes, impacts and solutions to soil pollution. The Outcome document of the symposium, ‘Be the solution to soil pollution’ paved the way to the implementation of a coordinated set of actions to #StopSoilPollution.” (2)
Quoted Article (1):
“FAO reports on global land pollution unveiled. The size of the problem is known, the lack of data weighs. Now is certainly time to act
Pollution is here but you can’t see it. Especially the soil one which impacts on everybody’s lives putting at risk the sustainable development goals of the Planet. That’ s the key message expressed by the FAO during the launch of its new report last Friday. “Soil contamination affects the quality of agriculture generating a loss of productivity between 15% and 20″ explains Natalia Rodríguez Eugenio, earth scientist and member of the Global Soil Partnership Secretariat (GSP). A clear damage “that affects especially the most vulnerable individuals”, she adds, given that 4/5 of the people classified as poor in the world still live in rural areas and largely depend on soil for their economy and livelihoods.
Soil pullution triggers a chain reaction
We must be cautious, however, because data are most likely underestimated. Little is known about the real size of the process. But one thing is clear: the domino effect is encouraging the uncontrolled spread of the problem. Soil, for instance, “is one of the main recipients of contaminants” including nitrogen fertilizers, according to FAO. And soil pollution “can have irreparable consequences on human and ecosystem health.” Water, air, food and people. In short, no one is safe. “Ecosystem and human health are interconnected,” the report says. “Yet neither can be effectively addressed without tackling soil pollution.”
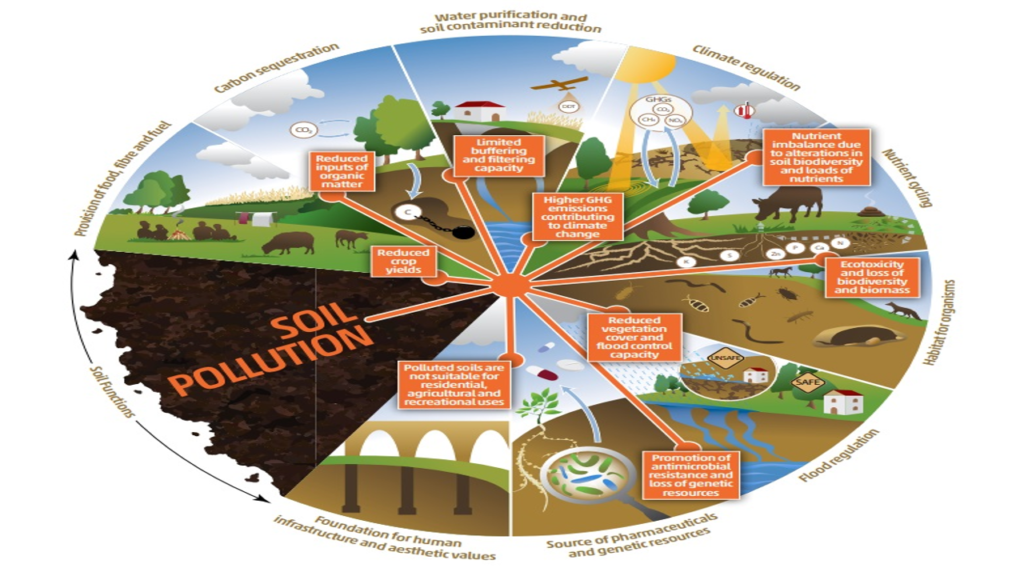
Soil pollution causes the reduction and eventually the loss of ecosystem services. Image: FAO and UNEP. 2021. Global assessment of soil pollution – Summary for policy makers. Rome, FAO. © FAO, 2021 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 IGO licence
Plastics and pesticides under scrutiny
The main sources of soil pollution “are industrial activities, mining, waste treatment, agriculture, fossil fuels extraction and processing, and transport emissions. There is, however, no concrete and comparable data on the actual emissions of each sector”. The truth, however, is that “since the beginning of the XXI century, the global annual production of industrial chemicals has doubled to approximately 2.3 billion tonnes and is projected to increase by 85 percent by 2030″ according to FAO.

EU Commission wants to reward farmers for their climate-friendly practices: Commission looks at new reward schemes for climate-friendly and sustainable farming practices with five sectors involved
Today, most part of the data come from the agricultural sector where the impact of contaminants is widely known. The greatest concerns are pesticides but also “the proliferation of organic contaminants and emerging contaminants such as pharmaceuticals, antimicrobials that result in resistant bacteria, industrial chemicals, and plastic residues.” The current pandemic, FAO says, has put pressure on the environment “with an intensified release of waste.”

Double-edged nitrogen is one more reason for a sustainable agriculture: How to manage nitrogen use to reduce environmental impact and protect soils. An Australian study provides guidance for firms and consumers
Europe is at risk
The analysis focuses as much on sectors as on geographical areas. The survey on European agriculture is especially interesting, covering 194,000 hectares of soil, or 25% of the continent’s land. “Agriculture represents a significant source of diffuse pollution in the region, mainly due to the use of agrochemicals,” the report says. “The analysis of agricultural soils sampled under the EU LUCAS survey showed that 80 percent of agricultural soils contain pesticide residues.” These include glyphosate and its derivatives, DDT and fungicides.
Nitrogen, whose presence reaches critical values in the runoff to surface waters in 65-75% of agricultural land in the EU. Three quarters of European soils, in other words, risk eutrophication. Also worrisome is the occurrence of elements such as arsenic, cadmium, copper, chromium, mercury, nickel, lead and zinc. “About 21 percent of agricultural soils in Europe present levels of cadmium above the regulatory thresholds” according to the report.

Glyphosate-treated soils say goodbye to invertebrates: A research from Mexico: the use of the controversial pesticide reduces the concentration of macroinvertebrates thus depriving the soil of their ecosystem services.
Global remediation and prevention
Although global distribution patterns are hard to define, the identification and assessment of pollution risk at potentially affected sites is a basic first step. Remediation operations are crucial and require shared expertise at the regional level. But prevention is still the best strategy. “In the current scenario of a worsening global trend in soil pollution,” the report says, “greater political, business, and social commitment is needed to seek alternative solutions to the use of highly toxic contaminants and increased investment in research, prevention and remediation.” Enhanced cooperation and partnership, in particular, “are essential to ensure the availability of knowledge, the sharing of successful experiences, and universal access to clean and sustainable technologies, leaving no one behind.” (1)
Sources and Reference:
1. Soil pollution is responsible for 20% of agricultural productivity loss. Author: By Matteo Cavallito
2. Global assessment of soil pollution. By: FAO, UNEP. Published by: FAO, UNEP, 2021
3. Peasant Protests in Europe. By: Christophe Golay. Published. On February 13, 2024
4. Peasants’ Rights and Protests, by Christophe Golay. Published: Globe, on 27. maj, 2024.

